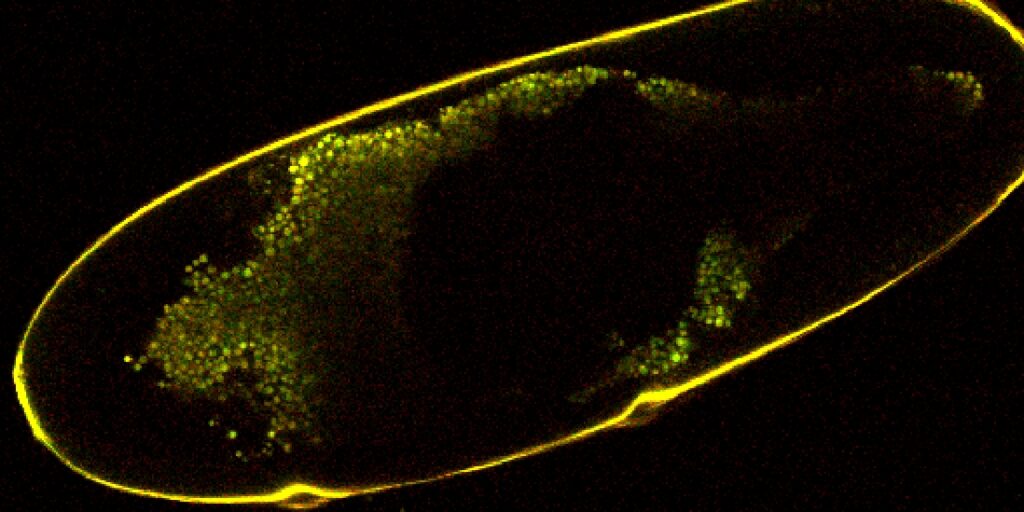
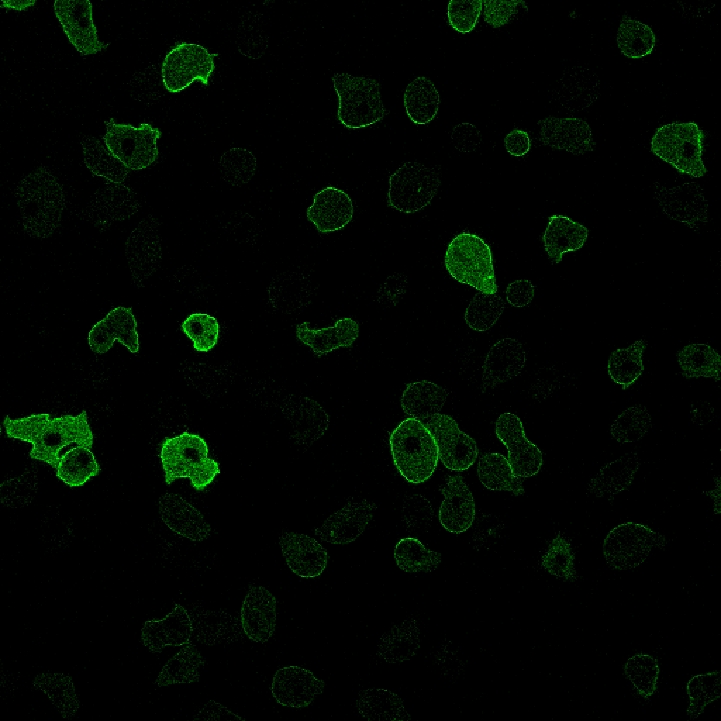
| Make Cell | Takes 2 input binary layers and filters them to include only cell and nucleus pairs with a specified cell area/nucleus area ratio. |
 |  |
| Clean | Gets rid of small noise. Built into most of the thresholding operations. Can use 3D version with the toggle. |
| Clean (3D) | Gets rid of small objects. Can choose matrix and radius threshold (used 10 here). Built into Threshold, but not Simple Threshold. |
 |  |
| Close Holes | Fills small holes inside binary regions. Can choose number of iterations, used 10 here on a binary generated by Threshold with no additional postprocessing and 25 iterations. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Close Holes (3D) | Another option to fill small holes in a 3D layer. Can choose matrix and number of iterations, unlike Fill Holes. However, using 10 iterations did not have much effect. |
 |  |
| Close inside Ref | Takes a parent binary layer (yellow) and a child binary layer (green) and closes holes in the child binary layer using a specified matrix and number of iterations. 3×3 and 10 iterations used here. |
 |  |
| Fill Holes | Fills holes in the binary layer. Built into most of the thresholding options. Can use 3D version with slider. |
| Fill Holes (3D) | Closes small holes in a binary layer. Built into Threshold but not Simple Threshold. Did not have much effect on the example image. |
 |  |
| Fill if Empty | If the connected binary has no {1} pixels, makes the entire binary layer {1} pixels. |
| Invert | Inverts the binary. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Invert (3D) | Inverts a binary. |
 |  |
| Separate Objects | Breaks binary objects up into smaller ones. Built into most of the thresholding operations. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Separate Objects (3D) | Separates nearby binary objects. Can select number of iterations (chose 5 here). Used color by ID on the binary layer to better show separation. Built into Threshold but not Simple Threshold. |
 |  |
| Separate Bright | Separates binary objects, using both binary and intensity layers. For bright objects on dark backgrounds. |
| Separate Dark | Separates binary objects, using both binary and intensity layers. For dark objects on bright backgrounds. |
| Smooth | Smooths out binary objects. Built into most of the thresholding options. 10 iterations used here. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Smooth (3D) | Smooths binary layer by using a sphere of the specified radius. Built into Threshold but not Simple Threshold. Used radius ~ 1 micron here. |
 |  |
| Smooth Objects | Smooths objects using an alternate algorithm. Compare to Smooth also using 10 iterations. |
 |  |
| Open | Uses Erode then Dilate, removing small objects. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Open (3D) | Uses Erode followed by Dilate for a specified number of iterations, which cleans up small noise while leaving bigger objects alone. Used 5 iterations here, which was enough to eliminate most of the small objects. |
 |  |
| Close | Uses Dilate then Erode, connecting objects and filling holes. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Close (3D) | Performs Dilate then Erode for a specified number of iterations, which closes holes in objects. Used 5 iterations here. |
 |  |
| Erode | Shrinks binary objects. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Erode (3D) | Compares voxels to their surroundings and sets {1} voxels to {0} if there is a neighboring {0}, which shrinks objects. Can choose matrix and number of iterations, used 2 here. |
 |  |
| Dilate | Expands binary objects. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Dilate (3D) | Compares voxels to their surroundings and sets {0} voxels to {1} if there is a neighboring {1}, which expands objects. Can choose matrix and number of iterations, only used 1 here and the binary region was still significantly expanded. |
 |  |
| Circular Open | Gets rid of binary objects under a certain radius, used 5 pixels here. |
 |  |
| Circular Close | Fills in holes smaller than the specified radius, used 10 pixels. Effect is most obvious on single cells. |
 |  |
| Circular Erode | Erode using a circle as its kernel instead of a matrix. |
| Circular Dilate | Dilate using a circle as its kernel instead of a matrix. |
| Circular Open/Circular Close/Circular Erode/Circular Dilate/Circular Clean/Circular Close Holes (3D) | Alternate methods of performing open/close/erode/dilate/clean/close holes, using a sphere of the specified radius instead of a square matrix of voxels. |
| Linear Open/Close/Erode/Dilate | Open/close/erode/dilate using a linear matrix as its kernel. Can select matrix and number of iterations. Will result in some lines. Linear Open’s effect on a cell with 15 iterations and a horizontal matrix shown. Can use Z version using the toggle. |
 |  |
| Linear Open Z/Linear Close Z/Linear Erode Z/Linear Dilate Z | More options for matrix-based image processing but use linear matrices in the Z-direction. Can choose number of iterations, the example here is 3 iterations of linear dilate, which has the effect of extruding objects in the Z direction. These options basically make objects more cylindrical and less conical. |
 |  |
| Centers | Puts a pixel at the center of binary objects. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Centers (3D) | Marks the geometric center of each binary object. |
 |  |
| Centroids | Puts a pixel at the centroid of binary objects, which differs from Centers because it takes the level of intensity underneath the binary layer into account and weights the centroid towards more intense areas. Can specify if signal is bright or dark. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Centroids (3D) | Marks the center of mass of each object, requires a color layer in addition to the binary to calculate density. Brighter parts of the image are weighted more. |
 |  |
| Connect Objects | Connects objects less than the specified distance apart with lines. Used 100 px (any smaller did not show an effect) and it took a VERY long time. |
 |  |
| Contour | Makes binary objects into 1-pixel contours. |
 |  |
| Convex Hull | Expands concave objects to make them convex. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Convex Hull (3D) | Extends object boundaries until objects become convex. Clearly encountered a bug in the example. |
 |  |
| Distance Function | Uses binary and original image to create a floating point layer that shows each pixel’s distance to the background pixels. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Distance Function (3D) | Creates a new floating point layer that stores each {1} voxel’s distance to the nearest {0} voxel. |
 |  |
| Geodesic Centers | Puts a single pixel at the geodesic center of each binary object, which is the closest point to all other pixels in the object that falls within its borders. Make Circle & Ring used to show pixels more clearly. |
 |  |
| Granulometry | Adds a granulometry floating point layer, which shows the grain size of binary objects. |
 |  |
| Homotopic Marking | Represents objects with single points, using a different method than center or centroid. |
| Inscribed Circles | For each object in a binary layer, replaces it with the largest circle that will fit within its borders. |
 |  |
| Medial Axis | Seems to look for midlines of objects, result similar to skeletonizing. Increasing endlines suppression will decrease branches. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Medial Axis (3D) | Marks each object’s medial axis, which somewhat resembles skeletonizing. |
 |  |
| Pruning | Debranches objects made by skeletonizing functions. Can choose number of iterations. |
| Ultimate Erosion | Uses Erode until one more iteration would remove objects. Can set how many iterations to keep. |
| Grow Objects | Grows objects by specified radius but prevents them from touching. Will make objects more convex. Used 15 px here. Might be useful for making borders smoother. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Grow Objects by Area | Grows objects until the area of the binary layer reaches the specified area fraction. If the area fraction is lower than the original binary layer, the binary layer is unaffected. Area fraction of 0.5 used here. |
 |  |
| Grow Regions | Takes a binary and color input. Extends binary objects to the specified intensity on the color layer. Can choose bright or dark regions. Used a lower threshold of 40 for bright objects. Might be useful if thresholding had to miss some parts of cells because of noise because it makes sure areas are connected to already detected objects. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Fast Exoskeleton | Faster algorithm for creating zones influence (but zones of influence does not have any speed issues). |
 |  |
| Make Circle & Ring | Creates 2 new binary layers from the input: the inside of objects and the border. Can also expand objects’ radius with Grow by and specify ring width. Used grow by 30 and width 10 px here. |
 |  |
| Thickening | Uses dilate to enlarge objects but prevents them from touching each other. until objects touch each other. Increasing parameter increases how much objects grow. Used Color by ID to show how objects remain separate and 30 iterations. |
 |  |
| Watershed | “Floods” image starting from either bright or dark regions, taking a binary and an RGB input. Essentially the inverse of zones of influence, ended up with a layer of {1} with 1-pixel wide {0} borders between regions using from bright to dark and the same but showing cell edges using from dark to bright. Will need to use Complement to see anything useful. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  From dark regions 🡪 complement
From bright regions 🡪 complement |
| Watershed (3D) | Floods regions from either bright areas to dark areas or dark areas to bright areas. This makes all of the space filled except for borders between objects. If binary is inverted, the boundary is left. |
 |  |
| Zones of Influence | Puts borders at the midpoints between objects. |
 |  |
| Skeletonize | Skeletonizes binary objects, which preserves their general shape while removing most of the area. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Skeleton (3D) | Skeletonizes 3D objects, which drastically reduces volume while keeping general extent of objects. |
 |  |
| Detect Branching | Puts single binary pixels at branch points of skeleton. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Detect Branching (3D) | Takes a skeletonized layer and puts voxels at branch points. |
 |  |
| Detect Endings | Puts single pixels at the end of branches. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Detect Endings (3D) | Puts voxels at ending points of a skeletonized layer. |
 |  |
| Cut Branches | Gets rid of branches smaller than the specified length. |
| Connect Free Endings | Uses a binary skeleton and RGB layer as inputs. Supposed to connect branches, with sensitivity determined by Connections input, but did not get it to work very well, and the algorithm was very time-consuming. |
| Vanish Small Objects | Gets rid of small binary skeleton objects using an RGB layer as comparison. Can specify diameter of objects to remove, as well as intensity threshold that determines if a small object is kept (because it has a high signal-noise ratio and is probably real data). Could not get it to work. |
| Remove Short Filaments | Shortens branch ends by the specified number of pixels. |
| Make 4-Connective | Changes pixels from 8-connected (pixels touching either adjacent or diagonally) to 4-connected (adjacent pixels only considered connected) by adding some. |
| Make 8-Connective | Switches connectivity from 4-connected to 8-connected by removing pixels. |
| Filter Objects | A filter for removing binary objects that also takes an RGB layer as an input. Lots of filter options to choose from, such as diameter, convexity, area, and perimeter. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Select Objects | Takes a table and a binary layer and selects objects that are represented in the table. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Select Largest Objects | Removes all objects in a binary layer except for the largest few. Can choose the number of objects to include. |
| Delete Objects | Similar to Select Objects, but removes objects represented in the table. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| (Remove Objects) Touching Borders | Gets rid of binary objects that touch the image border. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| (Remove Objects) Touching Frame | Gets rid of objects the specified distance or less from the image borders. Can change mode to keep objects touching the limit or not as well as choose from units. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Insert Line/Parallel Lines/Circle/Ellipse/Rectangle/Frame/etc. | Inserts a binary object. Can specify parameters/dimensions. Can also select mode: copy (deletes input layer), logical OR/AND, or subtract. Can insert a plane using the 3D version. |
| Color by ID | Colors the binary objects in the layer. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
 |  |
| Color by Value | Using a table and a binary layer, lets you color code binary objects by parameters. To use it, you have to go into the menu and select the columns. Clicking the gear will help create value ranges. Color coded by perimeter here. Can use 3D version with toggle.
|
 |  |
| Color by Value (3D) | Like 2D Color by Value, color codes objects based on values from an input table. Takes some work to set up. Colored by object volume in this example. |
 |  |
| Renumber Objects | Using a binary layer and a reference, reassigns object IDs in the binary layer to what they were in the reference layer. For example, if remove objects touching borders is used on a binary layer, a different object will have ID number 20 than the original layer. However, if Renumber Objects is used with the original layer as reference, the original object with ID 20 will have ID 20. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| Renumber Using Table | Another node for renumbering objects to their IDs from earlier in processing but takes a binary layer and a table. Must select a column to pull object IDs from. Can use 3D version with toggle. |
| TMA Renumber | Object numbering scheme for tissue microarray cores. Detects a square grid of cores and numbers objects based on position. Different from default binary numbering because it skips IDs of unfilled positions. |
| Add Borders/Crop/Change Canvas/Fit Size/Move/Resize/Resize to Ref/Rotate | Work like the Transformations section of preprocessing, but for a binary layer. |
| Connect | Accessible through 3D toggle. According to the NIS website this node connects 2D slices from adjacent layers into 3D objects and is not necessary because other options do this automatically. |
| Connect Cells | Accessible through 3D toggle. Connects objects that have a lot of overlap between neighboring layers and separates objects with less overlap. Has the overall effect of causing separation. |
| JS Postprocess | Open a JavaScript interface for coding your own image operations. Take RGB inputs by default but can change inputs to as many binary channels as needed. The only difference between the two is the data type of the output. |